23 Jan 2024
In the global pursuit of sustainability, Circular Economy has emerged as a revolutionary force, challenging traditional linear models and paving the way for a regenerative and environmentally conscious future. Throughout this article, we will delve into key approaches that define Circular Economy, examining how they contribute to a more sustainable and resilient global ecosystem.
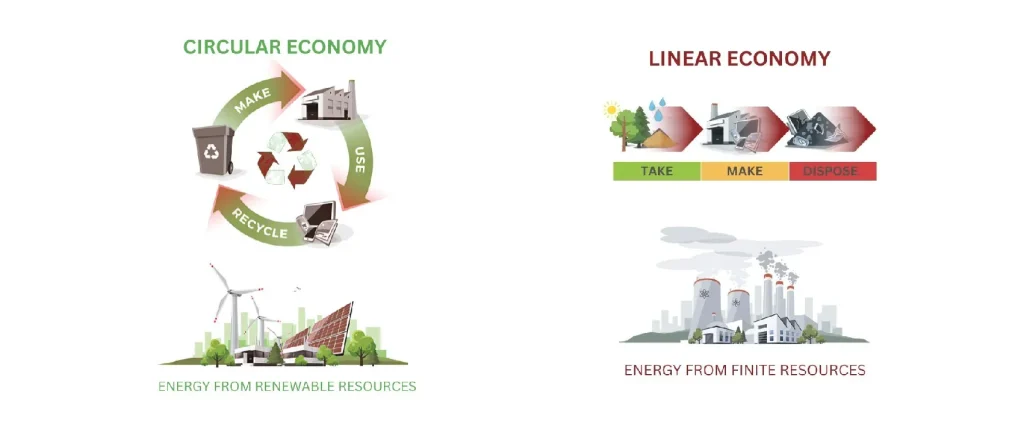
In a traditional linear model, often described as Take, Make, Use, and Waste, resources are extracted to create a product, which is then used until it becomes waste. This is clearly not a sustainable model, as all resources are ultimately limited and much energy is wasted every time we create a new product from scratch.
A circular model transforms this linear process by redefining waste as a valuable input back into the system. By promoting a closed-loop system, the circular model seeks to minimize waste and maximize the efficient use of resources.
Understanding the Circular Economy:
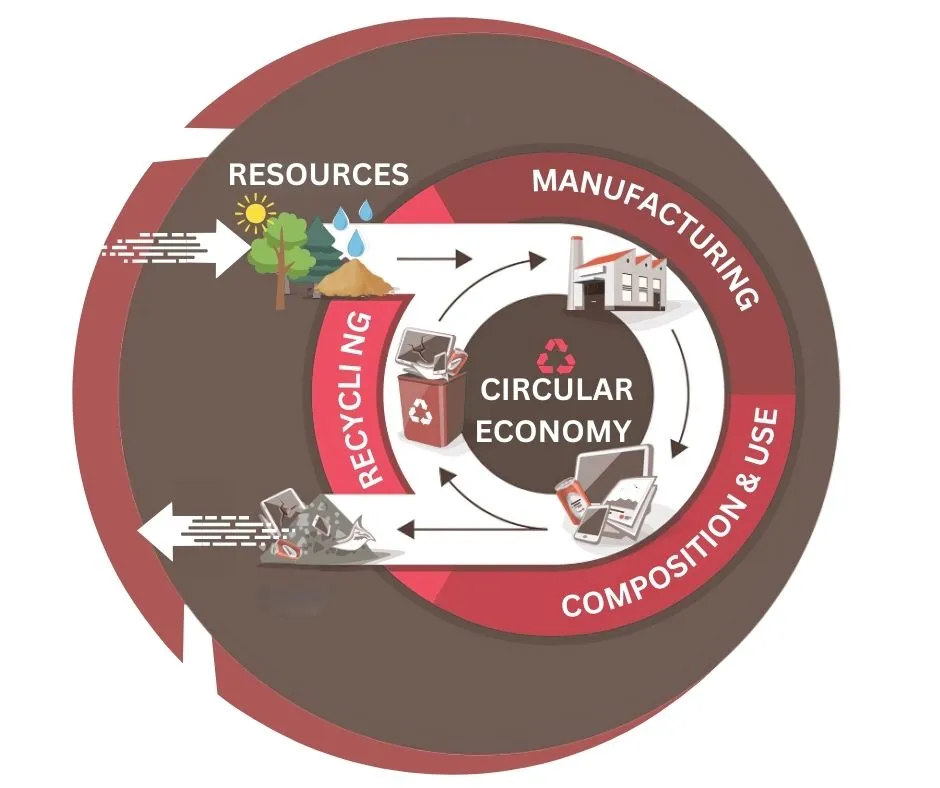
Circular Economy is a model of production and consumption designed to retain resources, including products, materials, and energy, within the economic system for as long as possible and at the highest possible value. This revolutionary approach seeks to establish a regenerative system by prioritizing the design of products for longevity, reuse, and recycling. Emphasizing the reuse of items rather than their outright disposal, Circular Economy has profound implications for industries, businesses, and individuals. Here are some key approaches that drive Circular Economy:
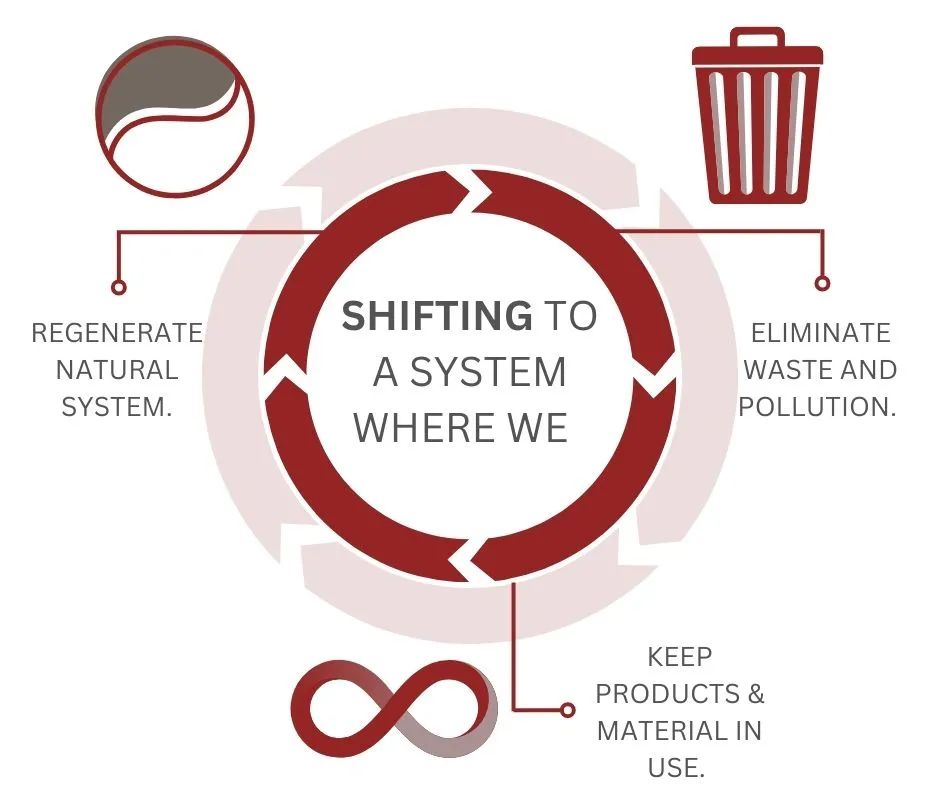
1. Eliminate Waste and Pollution:
In Circular Economy, the objective is to eliminate the concept of waste by redefining it as a valuable resource. Unlike the traditional linear economy, where products are discarded at the end of their life cycle, contributing to pollution and resource depletion, Circular Economy strives to design products and systems that minimize waste generation. This involves reducing the quantity of produced waste and finding innovative approaches to repurpose and recycle materials, ensuring their sustained value within the economic system.
2. Circulate Products and Materials:
This concept revolves around keeping products and materials in circulation for as long as possible, ensuring they retain their highest value. This involves several key principles:
– Rethink Design for Longevity:
Products are intentionally designed for extended lifespans, prioritizing durability and quality. This approach reduces the frequency of replacements and overall demand for raw materials. Businesses need to shift their focus from increasing revenues to offering longer-life and higher-quality alternatives.
– Reuse and Repair:
The Circular Economy encourages the extension of a product’s life through maintenance, refurbishment, and remanufacturing. This reduces waste and stimulates the growth of repair-oriented industries, fostering a culture of sustainability and resource optimization.
– Recycling and Upcycling:
Materials are recovered and reprocessed to create new products. In addition to traditional recycling, Circular Economy promotes upcycling—a creative twist that transforms waste materials into products of higher value. This showcases the potential for innovation within a sustainable framework, further minimizing the environmental impact associated with the production of new products.
3. Regenerate Nature:
The Circular Economy transcends the mere reduction of harm; it aspires to actively contribute to environmental regeneration. This commitment involves practices that restore ecosystems, promote biodiversity, and counterbalance any environmental degradation resulting from human activities.
Implementing a Circular Economy necessitates a transformation in product design and production, wherein waste is envisioned as feedstock for new products. This approach involves minimizing waste generation, thereby alleviating the burden on landfills and incinerators. Moreover, it significantly contributes to the reduction of environmental pollution and the depletion of natural resources.
Why Switch to a Circular Economy?
Embracing circular practices yields several advantages:

- Environmental Conservation: Circular Economy plays a pivotal role in environmental conservation by slowing the depletion of natural resources, diminishing reliance on raw materials, minimizing pollution, and mitigating the impact of climate change. The adoption of efficient and sustainable product design contributes to the reduction of energy and resource consumption. Furthermore, a shift towards products that are reusable, upgradeable, and repairable significantly reduces waste.
- Economic Opportunities: Adopting Circular Economy enhances competitiveness, stimulates economic growth, and opens up new economic opportunities. Businesses that embrace circular practices often discover increased profitability through heightened resource efficiency and innovative product design. The increasing demand for sustainable products creates a thriving market, offering consumers durable and innovative choices. This, in turn, promotes both environmental sustainability and innovation.
- Community Engagement: Circular Economy fosters community engagement through local initiatives, collaboration among stakeholders, and empowering individuals in sustainable practices. This shared responsibility strengthens social bonds and enhances community well-being. Reusing one company’s waste by another requires effective communication, consistent material availability, and collaboration among unlikely partners.
In conclusion, Circular Economy signifies a profound shift towards a more sustainable and resilient future. By re-imagining our production and consumption patterns, we can create a world where waste is minimized, resources are conserved, and the well-being of both the planet and its inhabitants is prioritized. Embracing Circular Economy is more than a choice; it’s a commitment to a regenerative and thriving world for generations to come. This transformative approach necessitates significant changes in businesses and across society. Consumers need to fully embrace the principles of reducing purchases, reusing products, and, when necessary, recycling.
The ongoing progress in various industries is encouraging. At MEHNA, we are at the forefront of these advancements. Our focus on sustainability drives us to develop innovative solutions that meet the highest standards of quality while promoting a greener future. By actively engaging in the Circular Economy, we contribute to a world where environmental conservation, economic opportunities, and community involvement work together to create a better tomorrow.